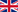
The Alay Mountains is a Central Asian mountains. The mountain range at an altitude of 5,544 m and a length of 400 kilometers. It stretches from west to east and partly forms a natural border between Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The Alay Mountains, specifically the area around the glacier Dara-i-Pioz (Darai-Pioz), is a known reference for many minerals.
The Alay Mountains is a Cordillera in Kyrgyzstan, the West end is in Tajikistan, it is a part of the Pamir of Alay system. It forms the southern edge of the Fergana basin is separated from Transalai mountains by 150 km of Alai Valley. The desert-like, about 400 km long Alay mountain reaches 5,539 meters above sea level; 811 km² are glaciated, mainly in the higher western part. At its westende it forms a mountain knot, from which of the Serawschankette and Hissargebirge branch off. In the eastern part the Alay Mountains is crossed by the highway Osh Khorog (Taldyk Pass, 3,615 m). On the northern slope in Chaidarken significant mercury mine.
The Alai mountain range is an extension of the Tian-Shan Mountains. It is located in the south of Kyrgyzstan and the western part reaches up to Tajikistan. The average height of about 400 km long mountain range is 4,900 meters.